Dual Dipole UHF RFID Tags
What are Dual Dipole RFID Tags?
Dual Dipole RFID tags are exactly what the name implies, a UHF RFID tag with a dual dipole antenna instead of a traditional single dipole antenna. The term ‘dipole’ or ‘dipole antenna’ in terms of an RFID tag is defined as “an antenna with a center-fed driven element for transmitting or receiving radio frequency energy.” (Source 1) In a dual dipole tag, two dipoles push RF energy into the center microchip instead of a single dipole.
Structure of a Single Dipole versus a Dual Dipole RFID Inlay
Most UHF RFID tags are rectangular in shape, with an antenna design that has two ‘open’ ends or poles, which harness the RF energy and deliver it to the Integrated Circuit or chip. To learn more about a UHF RFID tag’s structure and material composition – read our article “ RFID Tag Antennas”. Below are two examples of typical UHF RFID Single Dipole RFID tags.
Smartrac Shortdipole UHF RFID Tag
Dual dipole UHF RFID tags, however, are not all rectangular in shape like single dipole RFID tags. Dual dipole tags are mostly square to account for the second dipole, but they can also have a large rectangular appearance like the Confidex Crosswave. Below are 4 examples of popular dual dipole RFID tags, including the rectangular Crosswave.
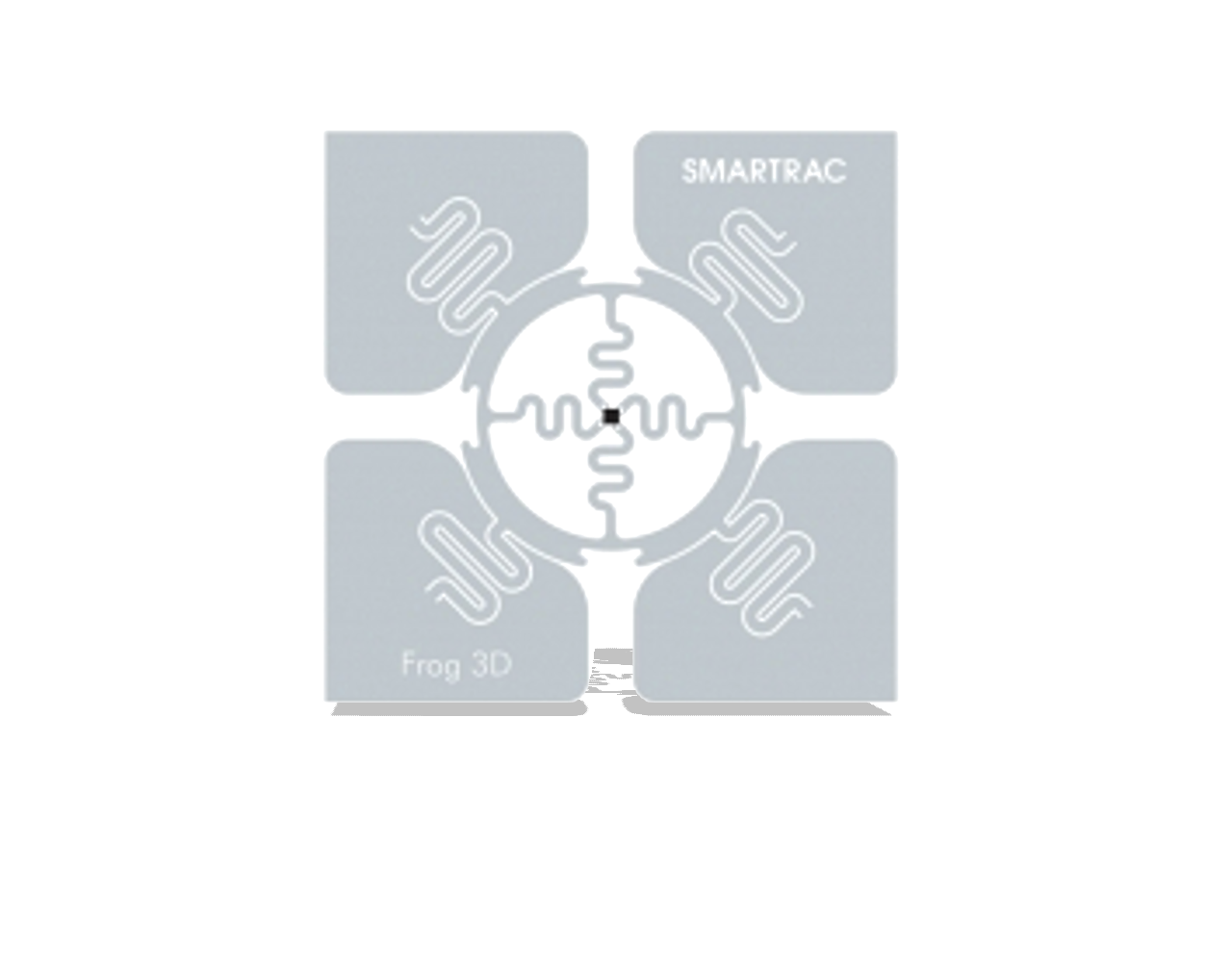
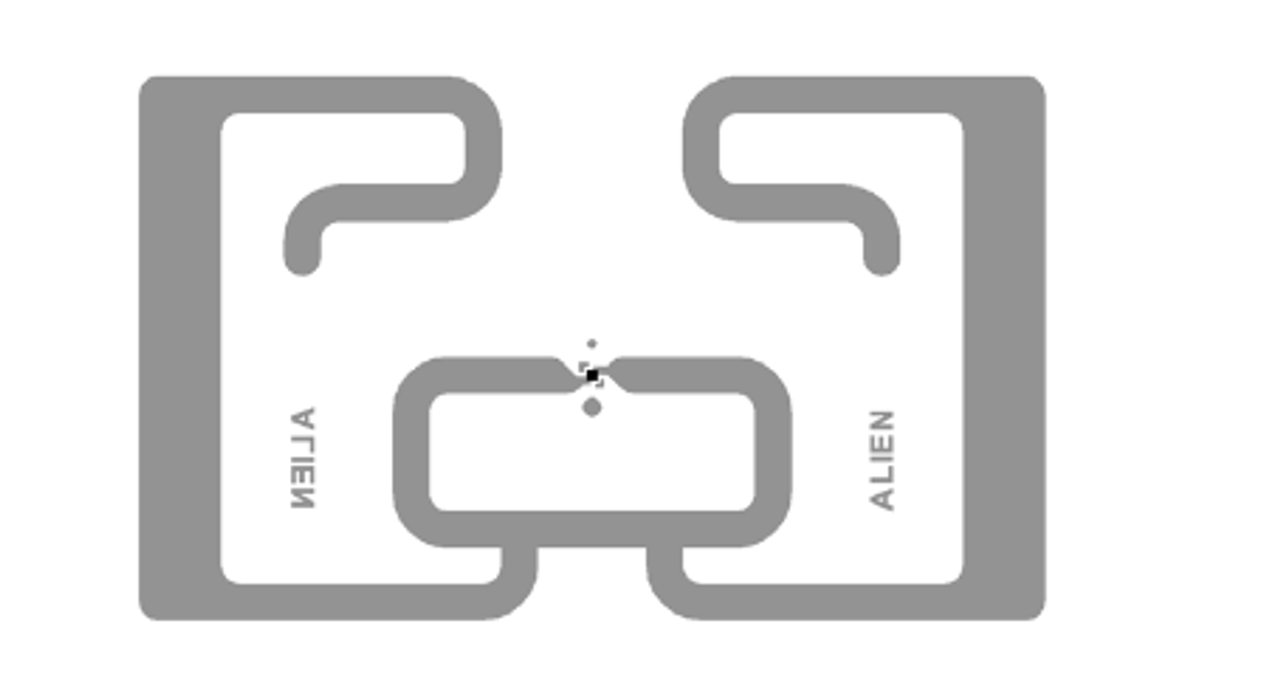
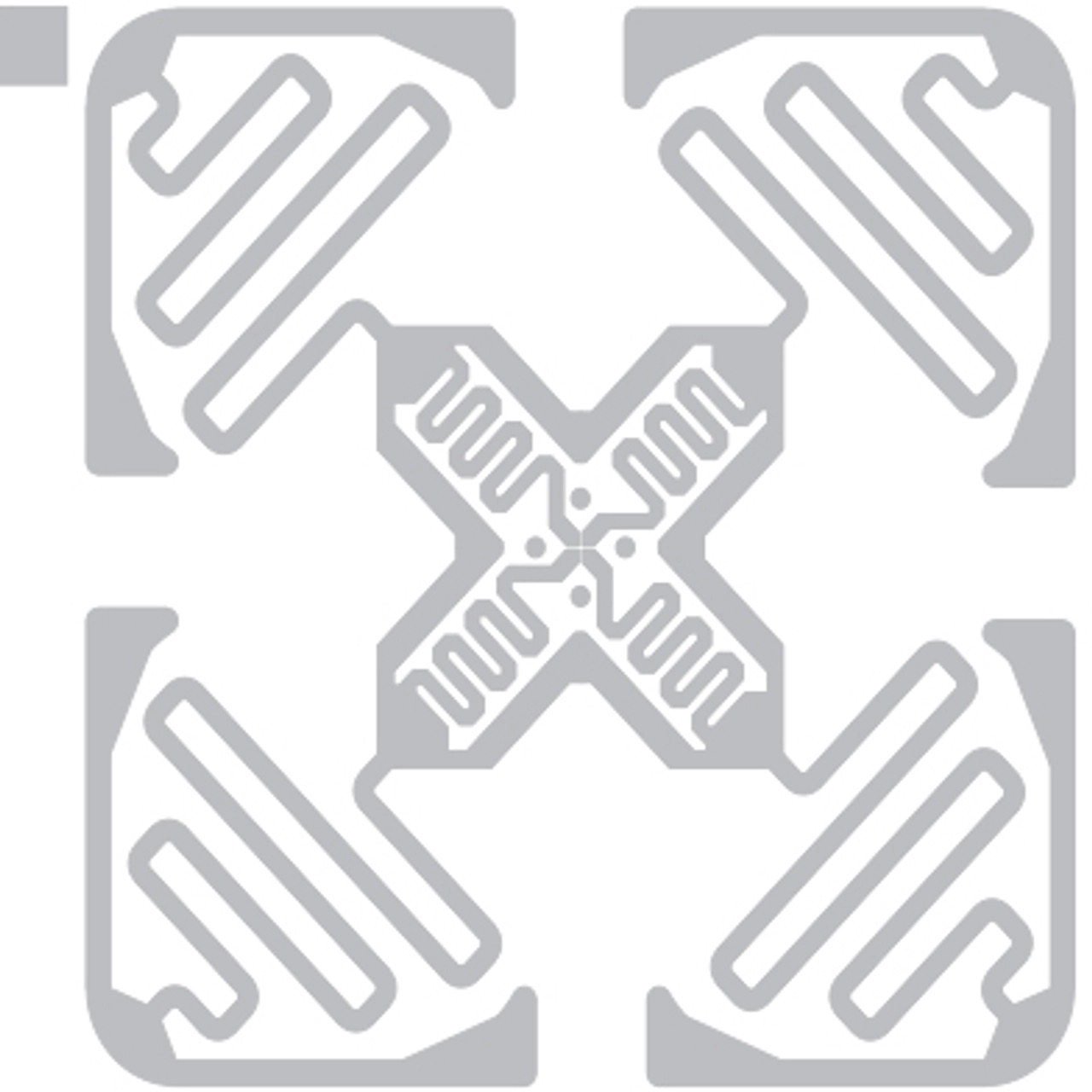

Confidex Crosswave Classic UHF RFID Tag
Pros of a Dual Dipole RFID Tag
The basic purpose of creating dual dipole UHF RFID tags is to provide tags with the capability of omnidirectional receiving and transmitting of RF waves. In some ways, dual dipole tags are similar to circularly polarized RFID antennas in an RFID system because they allow for reading RFID-tagged items regardless of tag orientation.
This can be very important in some applications that simply can't guarantee that the asset or tag will be traveling past the RFID antenna at a fixed orientation. For example, if a company is using an RFID portal system for shipment verification or logistics and a 3 rd party company is in charge of stacking packages on a dolly and maneuvering it past the RFID system – there is no guarantee the packages will be in the correct orientation to be read. In this example, if all packages were tagged with a dual dipole RFID tag, the orientation of the packages wouldn’t be an issue causing undue stress and missed reads.
Additionally, dual dipole RFID tags have a higher chance of being read in an RFID environment for two main reasons – the first being their structure. The two-antenna structure increases the chance of the tagged asset being read because there are two antennas operating on two dimensions at the same time. If most of the time the tagged asset will be in the correct orientation for the RFID antenna, then implementing a dual-dipole tag could function as almost a redundancy check for peace of mind.
The second reason dual dipole RFID tags have a greater chance of being read in an RFID environment is their large antenna surface area. Because dual dipole tags have twice the number of antennas, there is also more antenna surface area, which means that the tag can actually harness more RF energy. However, there’s no guarantee that dual dipole tags will get more read range than similar, single dipole RFID tags, as that greatly depends on each tag’s unique antenna shape and IC selection. Even though there isn’t an apples-to-apples comparison, the increase in the amount of space for harnessed RF energy makes dual dipole tags good testing candidates for any RFID application and environment.
Working with Dual Dipole Tags
Dual dipole RFID tags create an orientation-insensitive tagged asset that enables them to be used with linear or circularly polarized RFID antennas. Because an RFID system does not have to rely on a circularly polarized RFID antenna to provide the orientation insensitive aspect, RFID systems can use higher gain, linearly polarized RFID antennas to maximize read range.
It’s also important to note that even though dual dipole tags are orientation insensitive, they are still sensitive to other potential tagging concerns like size, angle, and placement. Be sure to walk through S(O)AP before deciding on the perfect placement for your RFID tags in our article “ 6 Factors that Affect RFID Read Range”.
Applications that Use Dual Dipole RFID Inlays
RFID inlays with a dual dipole antenna structure are ideal for any applications that will not have control over a tagged asset’s orientation. Tag manufacturers suggest that this is most common for applications like logistics, returnable transit items (RTI), and supply chain management.
Conclusion
Thank you so much for reading this article about UHF Dual Dipole RFID Tags. Below are a few links to example dual dipole tags.
For more information about how a dual dipole tag could impact your applications, comment below or contact us!
Source 1: www.sciencedirect.com, https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/dipole-antenna#:~:text=A%20dipole%20antenna%20is%20an,or%20receiving%20radio%20frequency%20energy.

