Tracking Attendance with UHF RFID
Tracking attendance is popular in both schools and businesses worldwide for a variety of different reasons, depending on the industry and specific sector. Schools can not only receive additional government funding based on attendance records, but also improve their schools rating, both locally and nationwide. Large companies track attendance to ensure their employees are present at work, working their specific shifts and hours, and that information can be used collectively with other metrics to provide the company with meaningful data.
In this article, we are going to walk through what can be accomplished in businesses or schools in terms of accurately tracking employee or student attendance.
Tagging Considerations
How can you tag students/personnel -
Understanding RFID tag considerations is usually key to determining if UHF RFID could work for a personnel tracking application. Companies currently tracking personnel for a variety of applications rely on UHF RFID tags embedded in badges (see image below) because Identification (ID) badges are commonly used in building access control or for security purposes.

UHF RFID Badges are ideal because they hide the RFID inlay inside so the tag cannot be tampered with or removed. Plastic ID badges are durable but the proper placement and attachment method must be addressed to prevent missed reads and lost or stolen IDs. RFID Badges are generally attached to bookbags, lanyards, or belt loops, depending on the equipment setup and type of environment. Removal of badges from their proper placement should be discouraged.
Attendance Granularity
The amount of RFID hardware varies greatly depending on the amount of data and level of granularity needed to deem the application successful. Below, three levels of granularity will be defined in order to show how a system can vary in cost and equipment, and how a system can be customized for a specific purpose.
In each of these examples, the school provides each student with an UHF RFID integrated ID badge, complete with a unique matching barcode and a picture of the student for visual identification. Each student’s badge contains an EPC number, a unique number to identify each student, which is input into the school’s computer system and associated with the student’s information such as: name, address, emergency contact information, etc. Students are required to clip their RFID ID badge to the top of their backpacks and instructed not to remove them because they function as the sole identification method.
The scenarios in this article are intended to illustrate how UHF RFID can provide solutions for tracking attendance with varying levels of granularity. Any and all RFID deployments must be assessed on a project by project basis in order to determine the amount hardware and software needed to make the application successful. Checkout our guide, Deploying an RFID System: 20 Questions & Answers for more on getting started with an RFID project.
Tracking Attendance: Example 1
Purpose: Determine if a student has entered or exited the school
RFID Hardware: Low Level
Granularity Level: In/Out
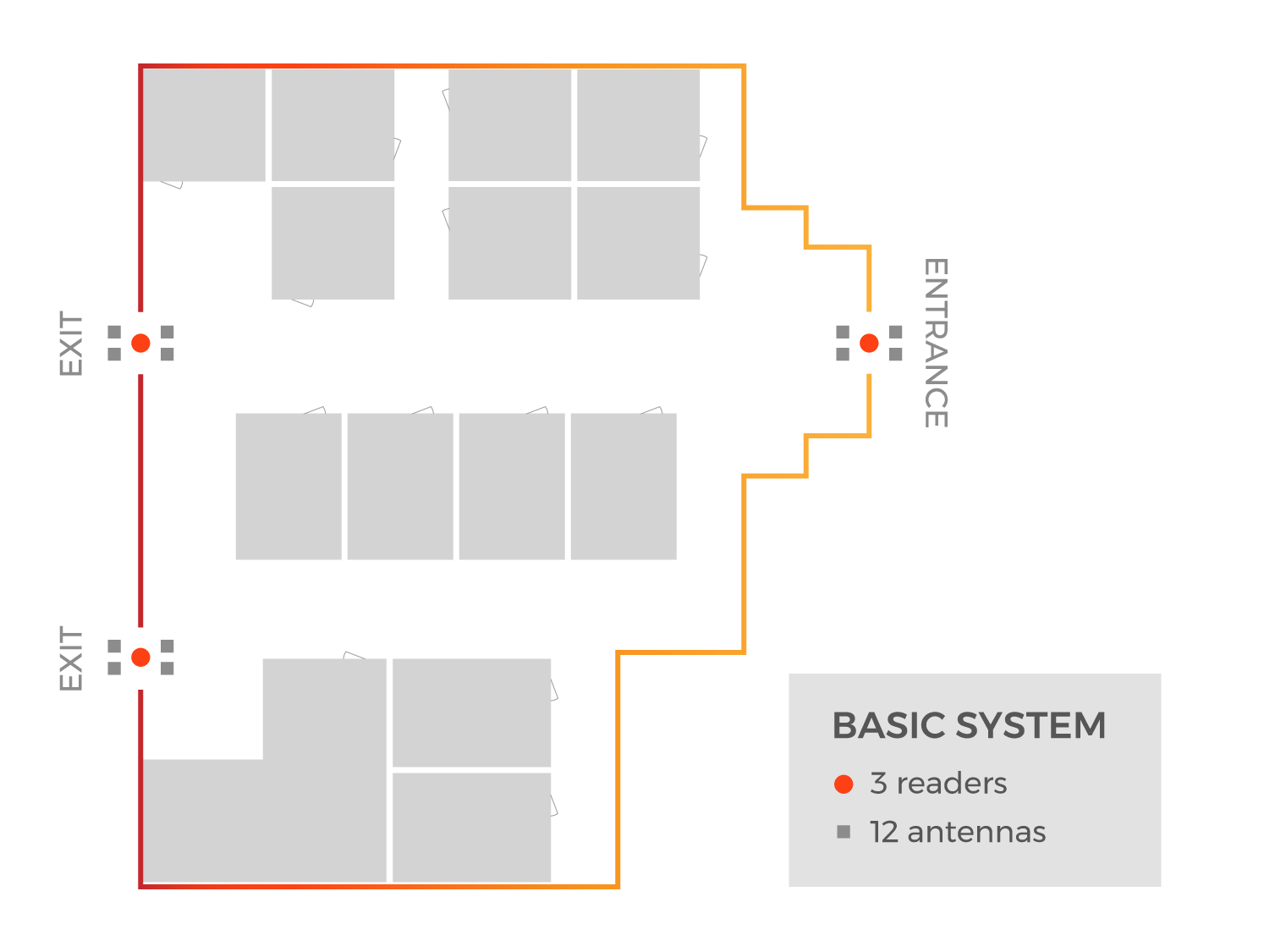
In this example, School X has decided to implement UHF RFID in order to document arrival and departure times of all students and use that data to automate the school’s attendance records.
Businesses -
In a business scenario, a similar setup could be implemented to automate the clock in and clock out procedure for the building or for a specific work zone.
The complex part of this system is determining which reads are “arrivals” versus which reads are “departures”. For this example, the school installed antennas on the outdoor overhang above each of the building’s exits. Inside the building, RFID antennas were installed on the building’s ceiling.
The rest of the solution is solved via software. Software can be programmed with logic that dictates something similar to the following:
Rule 1: When an RFID-enabled badge is read by Antenna #1 outside, followed by being read at Antenna #2 or 3 inside, the software can label that read series “arrival”.
Rule 2: When an RFID-enabled badge is read by Antenna #2 or 3 inside, followed by being read by Antenna #1 outside, the software can label that read series “departure”.
This is simply a demonstration software scenario, more information would be required in order to even create a piece of software similar to this one.
Another important aspect to this system is to ensure that each time a reader/antenna setup reads a tag, it qualifies as a ‘valid’ read, and not a ‘invalid’ read which would be a Student passing too close to an antenna and not actually leaving the building. Software is extremely important and can be setup to qualify each read based on RSSI, read rate, or a mixture of both or other indicators.
In any setup, including this one, the hardware, software, and logic should be thoroughly tested. The system will determine if the student is entering or exiting, and document that information along with the read data like Student ID number, date, and timestamp.
Tracking Attendance: Example 2
Purpose: Determine if a student is in the school and where
RFID Hardware: Medium Level
Granularity Level: Zonal Coverage
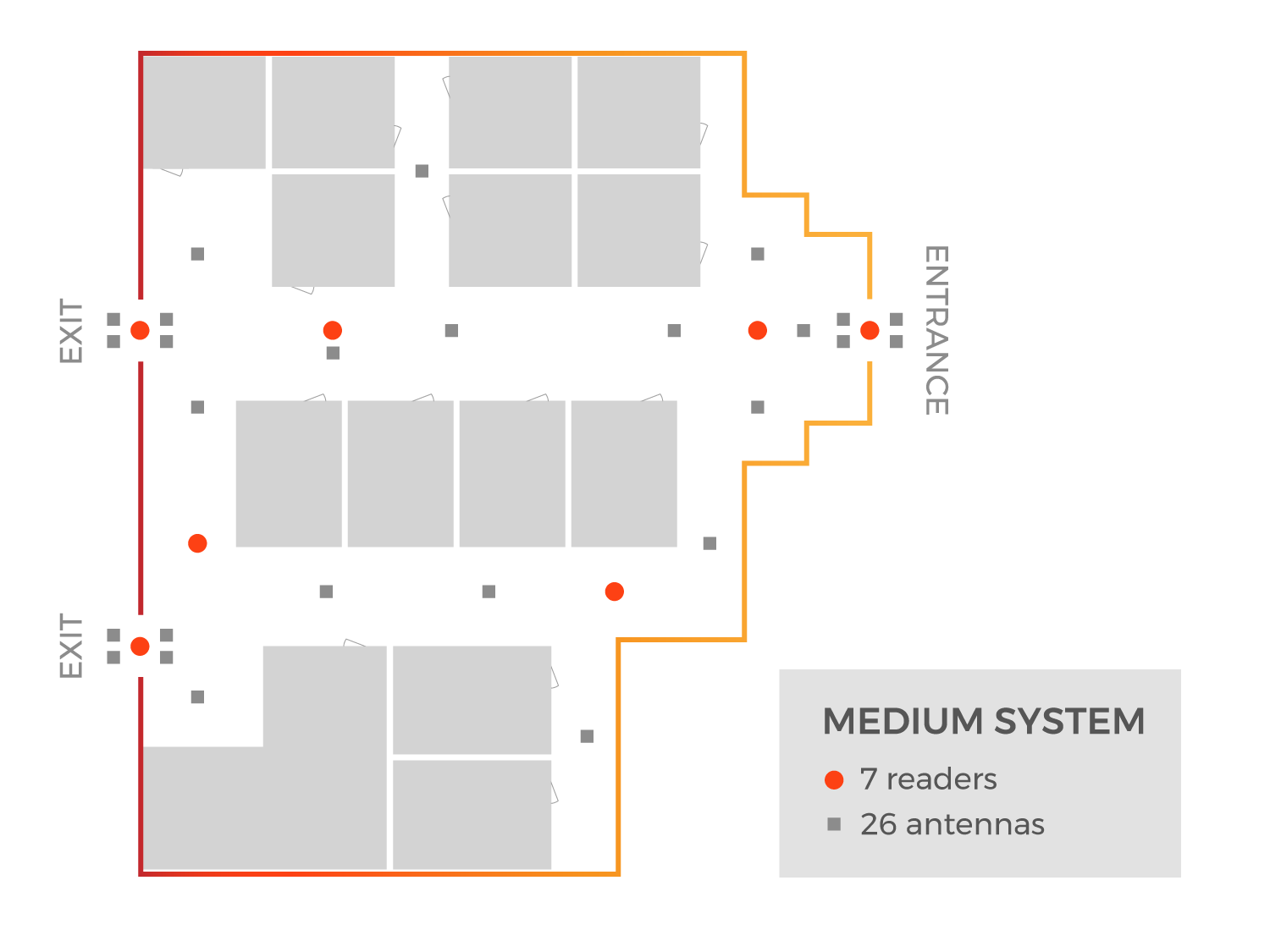
For this example, School Y has decided to implement UHF RFID in order to document multiple times a day which students are in the building and in which zone. The school will use the collected data for two main purposes:
1. In order to automate attendance records
2. To monitor hallways in between classes and after school hours.
Businesses -
In a business scenario, a similar setup could be used to monitor when employees are in specific zones, for example, the amount of time Employee A was in Safety Zone C.
School Y outfitted all entrances, exits, as well as hallways in the building with RFID readers and antennas. Because only these areas are monitored, no equipment is placed in classrooms. Depending on the size of the school and flow of the building, another option would be implementing strategic choke points in high traffic areas to ensure all reads are captured. When students are in the halls, their RFID ID badges will be read, but the tags will no longer be detected once the ID badges are in classrooms.
This can be accomplished by testing RFID reader power levels, read ranges, and possibly implementing RFID blocking materials. Using this method allows for the hardware to monitor the halls during class times and the software can be setup to create an alert if an ID badge is read in the hallway during certain times.
Tracking Attendance: Example 3
Purpose: Determine if a student is in the school; take individual class attendance
RFID Hardware: High Level
Granularity Level: Room Level Coverage
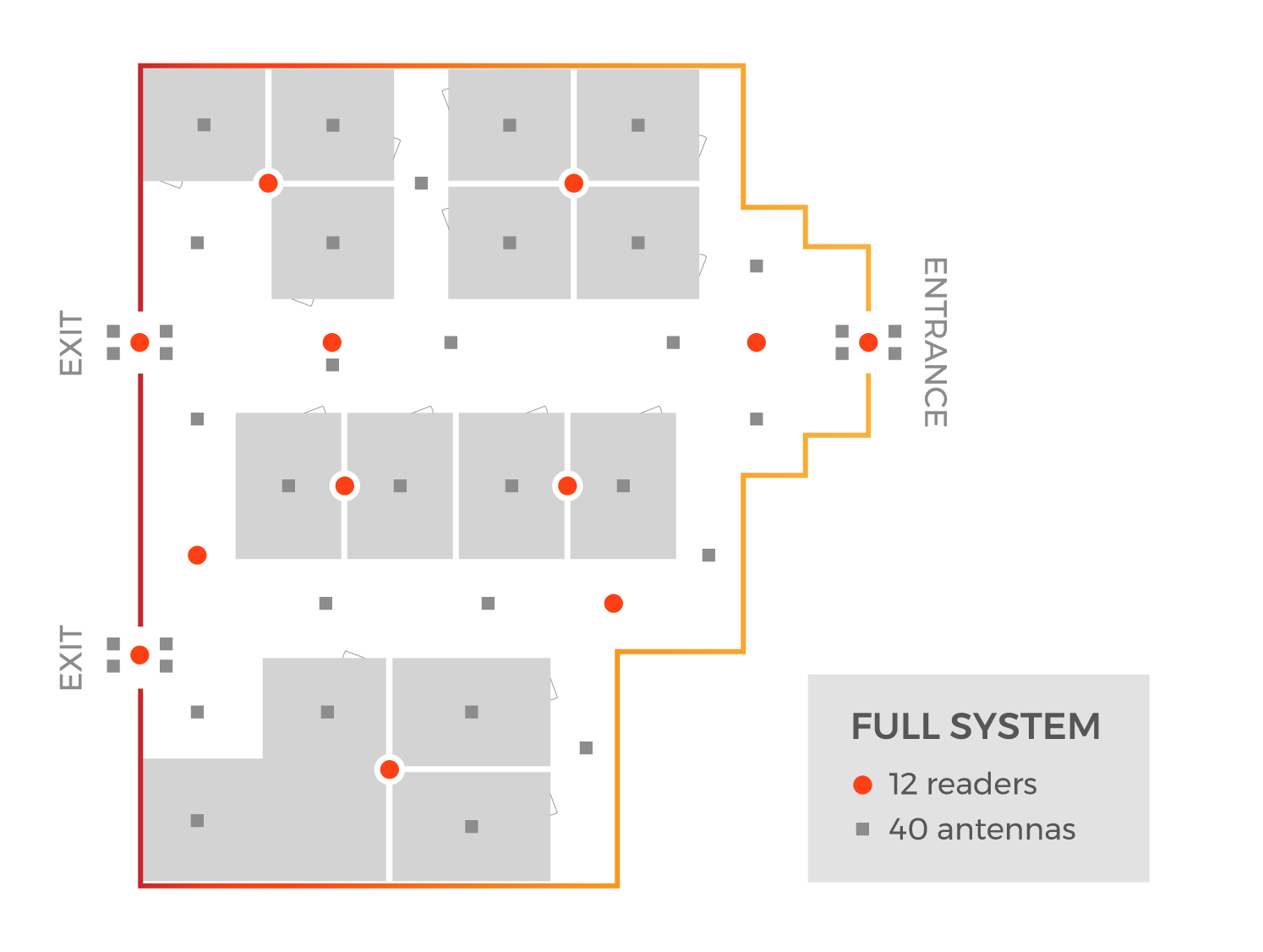
For this demonstration, School Z has decided to implement UHF RFID in order to take individual class attendance, which is popular, especially for college classes.
Businesses -
In a business scenario, this could be used to document employee time in cases where employees juggle multiple roles in different areas. Businesses could use a similar setup to determine the exact amount of time Employee A was using Machine B, which could be helpful data for several reasons -
1. A business’s HR Department could use this data for employee reviews, and as hiring data for determining if an additional employee is needed for a specific machine or task.
2. A business’s Operations Department could use this information to determine the number of hours logged on a machine for maintenance purposes or when determining when an additional machine or part is needed.
3. A business could use this information to examine longer, outdated processes and predict growth when paired with other company information.
School Z outfitted all entryways and exits, hallways, and classrooms. Within the application, each of the antennas is assigned a position so that the read data can be accurately collected and then allocated for the correct purpose – entering/exiting the building, in hallways, in a classroom. In this specific example, the added hardware is used to take individual class attendance for each classroom.
When an ID is read by a hallway antenna, and then transfers to being read by a classroom antenna, that read data can be used to update the attendance roster for that specific class via software. If the school would like to ensure that students stay the entire class, the reader can simply be programmed to turn on at specified intervals to inventory the room for tag ID’s.
What can this data be used for besides attendance records?
Schools:
Businesses:
Conclusion
If you’d like to learn more about all things RFID, check out our website, our YouTube channel , comment below, or contact us.
To read more about applications that gather data by tracking individuals, check out the links below!
What is RFID Event & Attendee Tracking?
From Marathons, to Mountain Bikes, to Motocross - Timing Your Race with RFID
