RFID Portal Readers vs. RFID Gateway Readers
When a company decides to automate their RFID tag reading instead of using an RFID handheld reader, one of the big questions they ask is – should I implement an RFID Portal system or an RFID Gateway reader/system. In this article we will walk through the similarities and differences of the two and when to choose which.

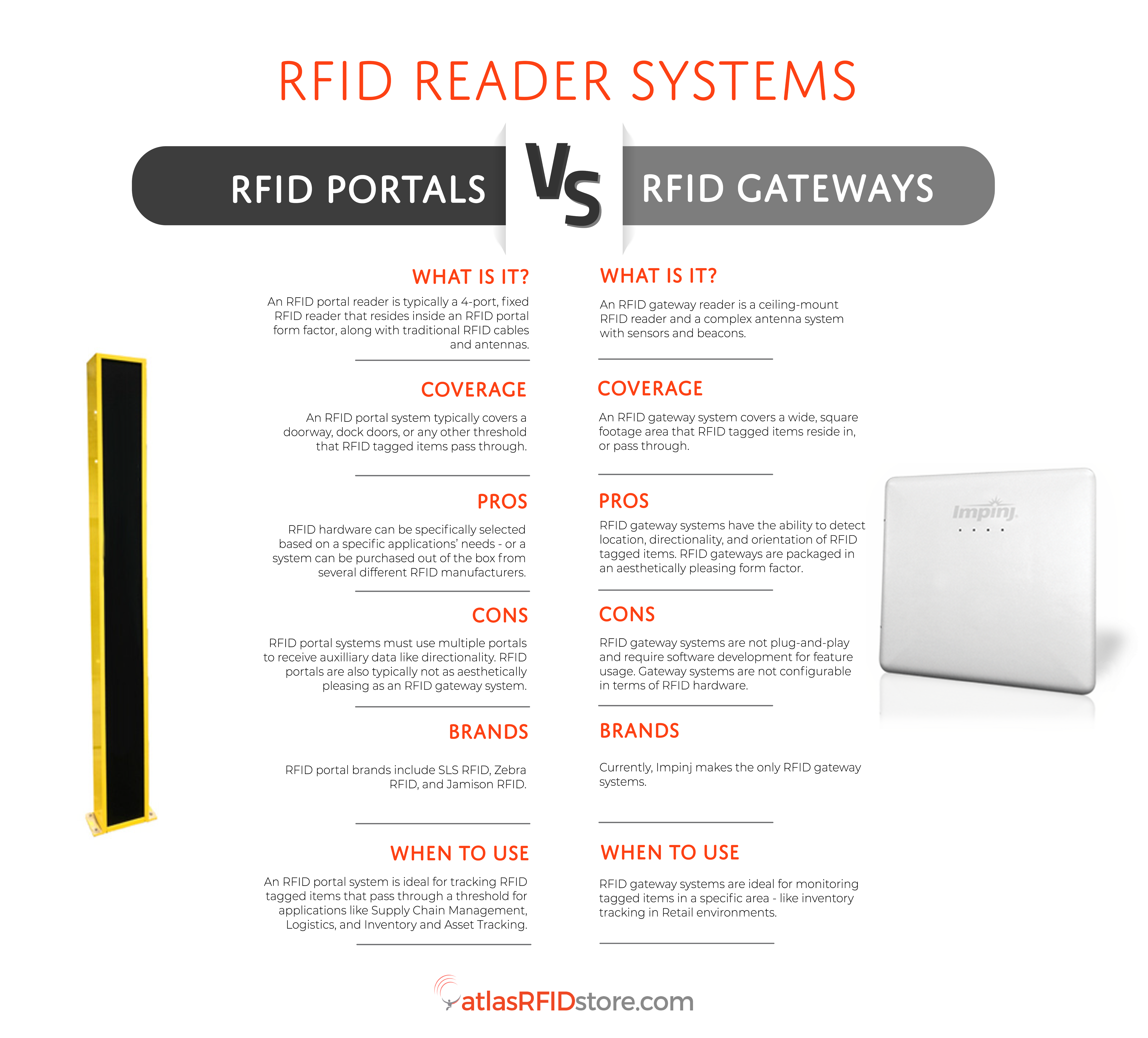
What is an RFID Portal Reader?
An RFID Portal Reader is typically a 4-port, fixed RFID reader that resides inside an RFID portal form factor. Many 3rd party companies as well as RFID reader manufacturers make RFID portals in order to read RFID tagged objects that pass through. An RFID portal works by creating a threshold through which the RFID-tagged items must pass through in order to be read. Most RFID portals are stationed at dock doors, or in a doorway between two rooms. Additionally, small RFID portals can be on either side of a conveyor belt or other type of manufacturing line so that products automatically pass through.
Some RFID portals contain all of the RFID hardware inside a plastic radome, while others basically use mounting brackets to mount the antennas and secure the reader to a basic pole system. Each portal typically contains one 4-port RFID reader and between 4 and 8 UHF RFID antennas, depending on the size of the portal and the number of read points required. RFID portal systems can also include GPIO devices such as light stacks and annunciators.

What is an RFID Gateway Reader?
RFID Gateway Readers are ceiling-mount RFID reader and antenna systems that allow businesses to monitor RFID tagged items in near real-time. Gateway RFID readers have a complex antenna array that allow users to track RFID tag location and direction. Currently, Impinj and Zebra are the only manufacturers of RFID gateways.
Gateway RFID readers are able to fit into the space of a standard ceiling tile and locate all RFID-tagged items within a 1,500 sq ft area, making these readers ideal for retail environments. Inside the RFID Gateway system is one of Impinj or Zebra’s leading RFID readers along with an array antenna with multiple beams. RFID gateway readers are easy to install, requiring no additional cable or external antennas.
Similarities and Differences - RFID Gateway Readers and RFID Portals
Similarities:
- Both RFID gateway readers and RFID portals contain all of the RFID hardware needed for an RFID system to function; however, you can build your own RFID portal by purchasing all components separately and mounting to a pole or truss.
- Both RFID gateway readers and RFID portals can be used to determine RFID tag directionality; however, RFID gateway readers have this feature more natively than RFID portals. RFID portals can be set up in a specific way with software logic to create this functionality.
Differences:
- RFID portals are not used for wide area coverage, but instead are used to read RFID tags as they pass through. RFID gateway readers are used to continuously monitor a specific area and report RFID tag reads within that specific area.
- RFID portals can be made DIY style, or purchased from a manufacturer like SLS RFID, Zebra, or Jamison RFID. RFID gateway readers are currently only made by Impinj or Zebra.
- RFID portals are slim, plastic, rectangular radomes, placed on either side of a threshold. RFID gateway readers are square/rectangular, aesthetically pleasing radomes that blend in with ceiling tiles to be unobtrusive.
When to Use RFID Portals?
RFID portal systems are ideal for reading RFID tagged items going in and out of a threshold like a dock door, loading dock, warehouse doors, or even from room to room. RFID portals are dock doors enable applications like logistics management, inventory management, supply chain visibility, laundry tracking and management, and rental item management.
When two portal systems (four individual radomes) are set up a few feet apart, RFID portals can be used with software logic to determine directionality – specifically when tagged items are leaving versus when tagged items are entering a facility. More aesthetically pleasing RFID portals can also be placed in customer-facing environments to track attendee movement in conferences and trade shows, hospital personnel movement, and track theft in retail locations.
When to Use RFID Gateway Readers?
RFID gateway readers are most often used in tag-dense environments without a large number of frequent movements. Gateway readers are most often used to track retail goods in a retail environment or inventory/assets in a back room or area. Gateway systems are ideal for covering a specific square footage area and monitoring the RFID tagged items that reside in that area, which is why retail item management is where they are most often used. Impinj’s xSpan gateway reader can be mounted at a dock door, similar to an RFID portal; however, it has a smaller form factor and only mounts on one wall instead of on either side of a threshold like a traditional RFID portal.
Conclusion
If you have implemented an RFID portal or RFID gateway, tell us about your personal experience in the comments below! For more information on RFID portals and RFID gateway readers, contact us!