Types of Memory in Gen 2 UHF RFID Tags
Updated: 7/17/2024; Originally Published: 5/01/2013
Gen 2 UHF RFID tags are comprised of an antenna and a chip (more accurately called an integrated circuit, or IC). In this article, we will walk through the 4 memory banks on the IC inside of a UHF RFID tag and when to use each. Gen 2 tags contain four types of memory:
- Reserved memory
- EPC memory
- TID memory
- User memory
When starting your application and selecting an RFID tag, in order to know about how much memory is on each tag's IC, you can check the specifications page on each tag's data sheet. Or take a look at our UHF IC RFID Comparison Guide.
Take a look at the graphic below for more information about each RFID tag memory bank.
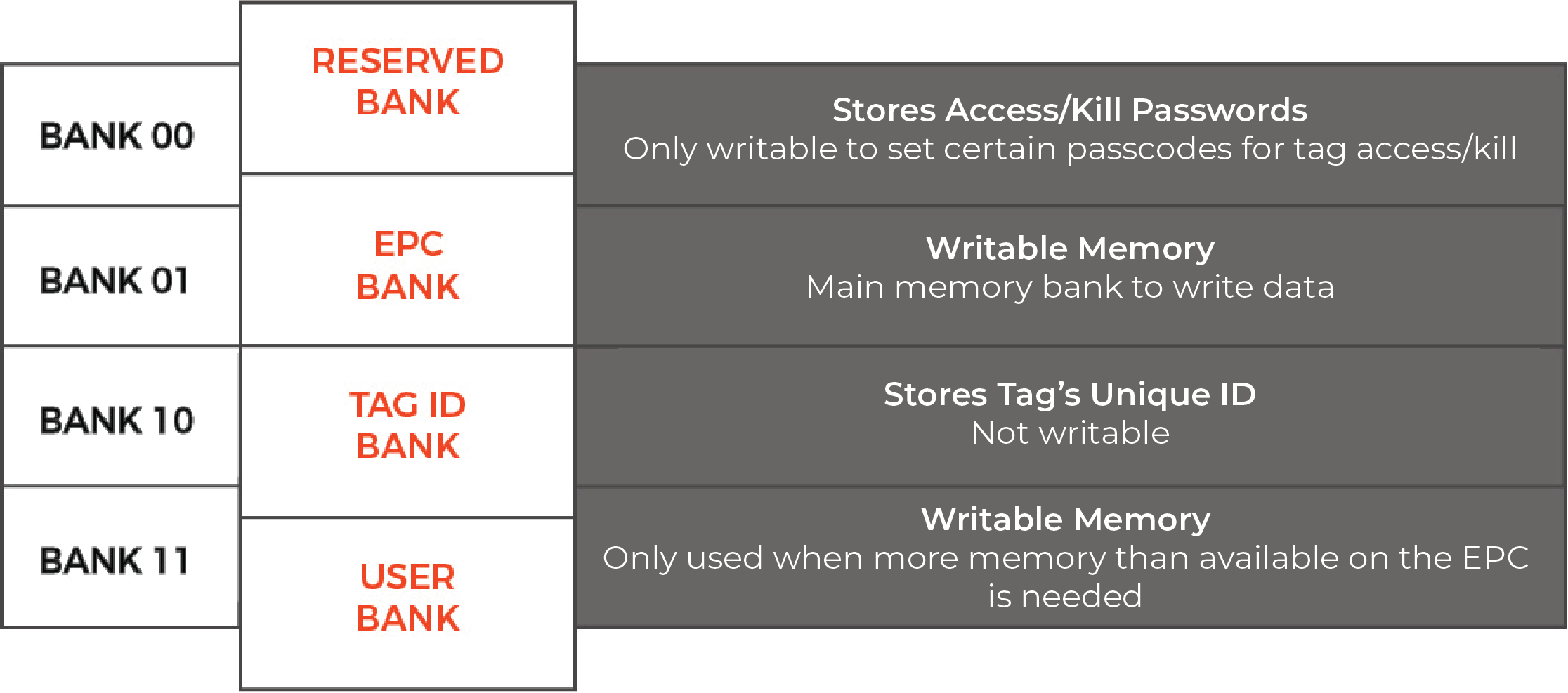
Reserved Memory
- Important Information: Stores Access/Kill Passcodes
- Writable: Only to update passcodes
This memory bank stores the kill password and the access password (each are 32 bits). The kill password permanently disables the tag (very rarely used), and the access password is set to lock and unlock the tag's write capabilities. This memory bank is only writable if you want to specify a certain password. Most users do not use this memory area unless their applications contain sensitive data. It cannot store information besides the two codes.
EPC Memory
- Important Information: Main Writable Memory
- Writable: Yes
This memory bank stores the EPC code, or the Electronic Product Code. It has a minimum of 96 bits of writable memory. The EPC memory is what is typically used in most applications if they only need 96 bits of memory. There are some tags that have the capability of allocating more bits to the EPC memory from the user memory. EPC memory is your first writable memory bank.
TID Memory
- Important Information: Tag's Unique ID
- Writable: No
This memory is used only to store the unique tag ID number by the manufacturer when the IC is manufactured. Typically, this memory portion cannot be changed.
User Memory
- Important Information: Extra Writable Memory
- Writable: Yes
If the user needs more memory than the EPC section has available, certain ICs have extended user memory which can store more information. When it comes to user memory, there is no standard in how many bits of memory are writable on each tag. Typically, the extended memory is no more than 512 bits, but there are some high memory tags with up to 4K or 8K bytes of memory. This is the second writable memory bank for Gen 2 ICs.
Conclusion
If you have any questions regarding regarding Gen 2 RFID tag memory or anything RFID related, please don't hesitate to contact a sales engineer at atlasRFIDstore.com by emailing sales@atlasRFIDstore.com or calling (205) 383-2244. If you would like to learn more about all things RFID, check out our website, our YouTube channel, comment below, or contact us.
To read more about RFID Tag Memory Banks, check out the links below!
